Have you ever done a technical audit on your site? You can’t have a robust technical SEO strategy without proper and regular auditing. But why?
Whether you’ve never performed a technical SEO audit, or you’re working to optimize your auditing process, this post is for you.
Today we’ll cover:
- What is a technical SEO audit
- What’s behind a great audit
- Common technical SEO issues to avoid
- How SEORadar helps you keep an eye on your website’s code
Let’s get started!
First Things First: What’s a Technical SEO Audit?
Few websites rank on Google without intentional SEO efforts. Getting ranked on search engines is largely dependent on an effective SEO strategy. The first (and key) step is to properly structure and optimize your website.
This is where technical SEO comes into play.
Technical SEO involves formatting your website’s data so search engines can understand it. Essentially, technical SEO covers all the elements that make your website easier to crawl.
These elements include:
- Meta titles & meta descriptions
- Your Robots.txt file
- Your XML Sitemap
- Server responses (2XX, 3XX, 4XX, 5XX)
- 301 redirects (permanent) and 302 redirects (temporary)
- HTTP headers
When talking about SEO, most people think about link building and content strategy, not technical SEO. But even if you have interesting, high-quality content, if the search engine can’t crawl your pages, you won’t get ranked. Without solid technical SEO, your website’s structure could sabotage your content efforts.
So, how can you make sure none of the aforementioned elements affect your site’s crawlability? Conduct a technical SEO audit and use those insights to optimize your platform.
But wait, technical SEO audits must be approached in a careful and focused way, taking into account each potentially problematic element, to get a better understanding of what’s going on.
In the next section, we’ll dive into common technical SEO issues and how to detect them.
Common Technical SEO Issues & How to Detect Them
You can’t have a healthy platform without regular technical SEO audits. But, if you’ve never done an audit before, you may feel a little overwhelmed. Sometimes, after completing an SEO audit one realizes that certain details were overlooked. And those details may be the source of major indexability problems.
Thus, if you want to conduct a successful technical SEO audit, don’t overlook:
- Crawling capability
- Indexing capability
- Ranking capability
- User experience
- On-Page optimization
Let’s explore each of these dimensions, what problems may appear, and how to solve them.
Crawling Capability Issues
The first thing you should check when performing a technical site audit is crawlability. Bots will crawl your pages to gather information about your site, so they must be easily accessible.
If for any reason, the bots can’t crawl these pages, they won’t be indexed, nor ranked.
Quite simply, preparing a site for crawling is akin to paving the road that search engine bots will take to travel through your website.
So, how should you get started? Make your pages easy for the bot to navigate.
Make sure you provide:
Canonical tags

Use canonical tags to tell search engines what’s the preferred version of a duplicate page.
An XML sitemap
Create an XML sitemap to help bots understand your site structure. Make sure that this map:
- Only contains canonical tags
- Doesn’t contain 404s
- Is kept up-to-date
A clear website structure
Create a consistent site structure. This won’t only help bots, but also users. Make sure that:
- You’re grouping content in a way that’s intuitive (especially when it comes to products and posts)
- Your most important pages are easier to find than hyper-specific landing pages or blog posts
- Every page and post has a well-defined topic and intent
URL indexing
Check that all URLs have been indexed. On Google, you can verify which URLs are indexed by searching “site:[nameofsite.com]”.
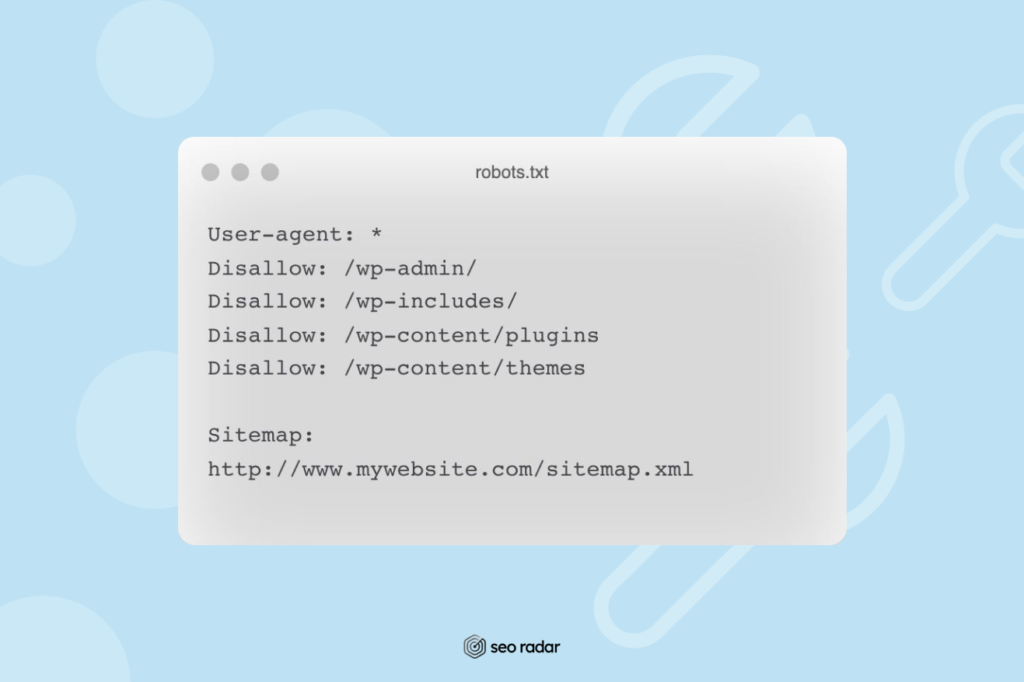
Robots.txt
Set up your robots.txt correctly. By using specific directives, robots.txt files suggest which URLs should or should not be crawled by search engines. Plus, with Robots.txt, you can remove any invalid URLs from crawling.
Pro-tip: The directives on robots.txt are just suggestions. To prevent your content from getting indexed more strictly, use “noindex” tags. You can read more about them in our duplicate content guide.
Noindex tags
Now that we’ve mentioned “noindex” tags: Check whether your “noindex” tags are configured correctly. These meta tags tell search engines not to index the URL they’re in. So, verify whether you’ve applied “noindex” tags to the wrong pages.
Broken links
Fix or redirect any broken or suboptimal links. Verify that all redirects have been set effectively. Looping redirects can affect your site’s URL recognition.
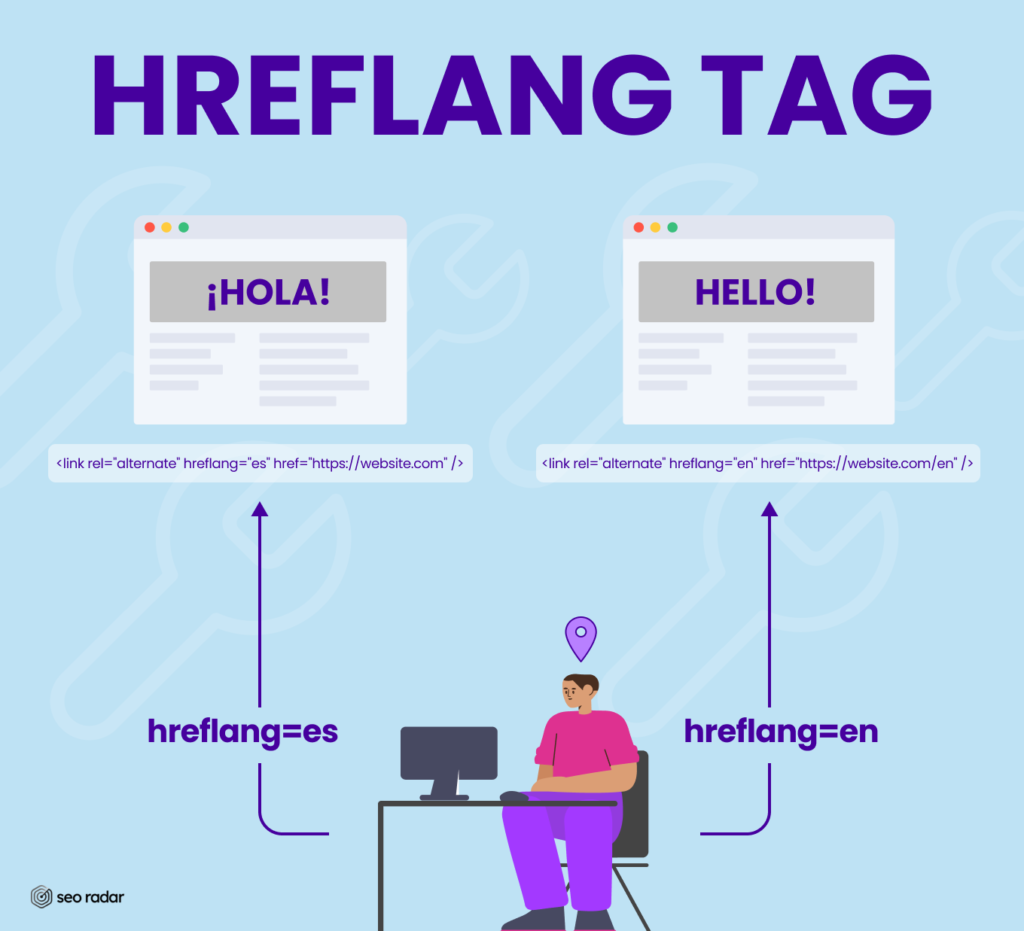
Hreflang tag
Thanks to hreflang tags, your users will be redirected to the appropriate page based on their language or search location. If you don’t run a multilingual site, this tip isn’t relevant to you. But, if you do: Ensure that your localized versions are well-differentiated, through properly applied hreflang tags.
Pro-tip: Google doesn’t like websites with two different languages on them. For instance, an English main page and a Spanish blog. If that’s how you’re currently running your website, use hreflangs to let Google know which content should be delivered to each audience. If your blog isn’t available in English, provide a fallback.
Clean code
Check that your CSS and JavaScript files can be crawled. Keep in mind that you should use crawlable HTML or your main navigation functions. That will benefit both crawlability and accessibility.
Thin content
Delete content that is of little or no value. These pages can be optimized with great and unique content, or blocked from indexation with a noindex tag.
Covering these bases early makes the rest of the technical audit much easier to perform. Now that we’re done with the basics, let’s move forward to indexing capability issues.
Indexing Capability Issues
Search engine indexing occurs when the search engine bots crawl your website, store your content, and, once indexed, decide which pages will rank in the SERP and where.
While you can avoid most indexing issues by reviewing all the points we discussed above, that’s not all.
You should also check for:
- The presence of 4xx client codes, such as 404 (not found) and 405 (method not allowed)
- Access to any URL denied by the server
- Misused nofollow tags, which may lead Google to believe that you are attempting to manipulate your position in search results
- 5xx codes server errors, which prevented a visitor from processing their request, including 500 (incorrect internal server address), 502 (bad gateway), 503 (service unavailable), and 502 (gateway timeout)
- 301 (permanent) and 302 (temporary) redirect issues. Sometimes, temporary redirects are meant to be permanent, which is why it’s important to track them
Last but not least, you shouldn’t forget to create and use SEO sitemaps. Sitemaps allow Google to identify and catalog your content more precisely. They are key to efficient indexing.
Ranking Capability Issues
As soon as the search engine crawls and indexes your site, you’ve got to figure out how to improve your ranking and compete.
At this point, the discipline becomes all-encompassing. Keeping a close eye on all contributing factors is the key to avoiding potential issues.
Let’s talk about two key factors:
- Quality content
- A well-configured internal and external link structure
Quality Content, No Duplicates
Google often adjusts its algorithm to improve the quality of its search results. When asked why the updates happen, Google will always reply “we tweak quality continuously”.
In the earliest days of SEO, you could game the algorithm by using your focus keyword constantly. But if you have the same focus term fifteen times in a paragraph, your content will be boring, redundant, and valueless to users. This may have worked years ago, but it’s not what search engines want today.
So, what do search engines expect?
In this day and age, Google is all about E.A.T.: Expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. If your content doesn’t provide unique and genuine value, it simply won’t rank.
Thus, you should avoid sending mixed signals with duplicate content. Duplicate content should be removed, updated, or redirected to the URL you want to rank.
Content should address the audience’s questions and match their search intent, without gimmicks and with useful information. By investing in quality content, you’ll also be likely to get high-quality backlinks (which are crucial for ranking).
Well-configured Internal & External Link Structure
Search engines use internal and external links to determine where the page fits within the query schema. Internal links improve crawling, indexing, and ranking.
But, you should be updating your content over time, and that could lead some of your best links to break.
When these links are optimized, they’ll take the user where they want to go, not to a 404 page. A linking error or an orphaned page (with no internal links) is perceived negatively by search engines.
Here’s how you can fix it:
- Redirect or update the link with the correct URL
- Remove the link
Your site’s SEO success is dependent on both quality content and efficient link building. By optimizing these dimensions of your site, you can achieve great ranking results.
User Experience Issues
In June 2021, Google announced that page experience affects ranking. Why?
User experience (UX) is extremely important for SEO, not just because it determines whether someone stays on your page or leaves, but also because Google takes it into account. A website that doesn’t take UX into account won’t succeed at SEO.
Everything boils down to one word: accessibility. Accessibility is at the heart of both user experience and technical SEO.
When performing a technical SEO audit, you should focus on:
Web Core Vitals
Web Core Vitals are speed metrics that are part of Google’s page experience signals. The metrics include content load time, page responsiveness, and visual stability.
Page speed
In 2018, Google introduced speed as a ranking factor for mobile devices. Slow sites not only get high bounce rates but also cause bots to crawl partially loaded versions with incomplete content.
HTTPS
Set your pages to use HTTPS instead of HTTP. While this is not a ranking factor, it shows users that your site is safe and prevents web browsers from blocking your traffic with security warnings.
Mobile-First
Google has been ranking websites based on their usability since 2015, so there are no successful websites that aren’t responsive. Make sure your website is beautiful and functional, even when accessed through mobile devices.
This list doesn’t cover all aspects of web accessibility, just the most relevant to a technical SEO audit. We encourage you to do your own research, as accessibility is fundamental to providing great digital experiences.
On-Page Optimization Issues
On-page SEO covers:
- Title tags
- Meta descriptions
- Header tags (H1, H2, H3…)
- Image alt-tags
- Internal linking
As your site grows, your old content may become unoptimized. Especially if you’ve migrated your site. Are you cannibalizing your keywords? Do all your pages have relevant meta descriptions? Are there any orphan pages or missing alt-tags?
Perform regular audits of your entire website to make sure that you don’t miss any optimization opportunities.
Don’t Lose Sight of your Code: Monitor Technical SEO Issues 24/7
In this post, we discussed the importance of a technical SEO audit to optimize website performance. But, beyond technical SEO audits, how can you make sure your technical SEO remains on point?
Monitoring your meta descriptions may sound like a time-consuming and almost impossible task. But don’t worry. SEORadar’s got you covered. Our technical SEO tool looks for changes to your website that might affect your ranking before they do.
SEORadar monitors over 100 elements, including:
- Redirects
- Indexing issues
- The removal of an important keyword from the headings or meta description
- Broken or inaccessible links on the sitemap
- 404 errors
- Robots.txt changes, hreflang tags, internal links, and much more
Plus, you get a personalized alert when these changes occur. Which changes are more important to you: keyword changes or sitemap changes? Are you more comfortable communicating via Slack, email, or text? It’s up to you. SEORadar is completely customizable and adapts to your workflow.
Don’t let an undetected change affect your SERP ranking. Start a free trial or book a demo today.